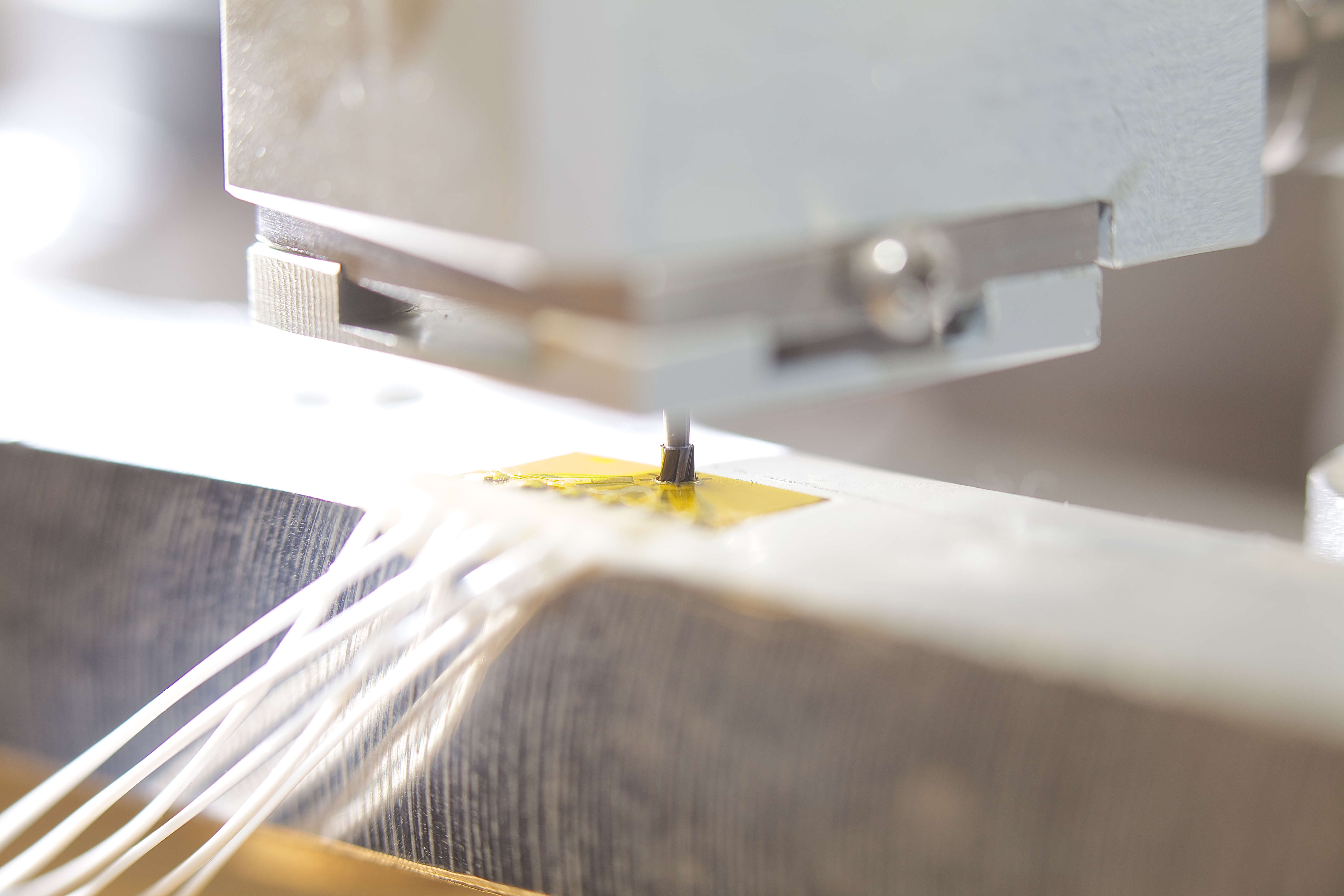
Hole drilling method
Residual stresses reduce load capacities and mechanical components safety during every day operations, that is the reason why it is important to analyze this kind of stresses due to prevent mechanical equipment failures. One of the most flexible, reliable and non-destructive technique for performing residual stress analysis is the hole drilling method. The hole drilling method gives an high level of accuracy and is, in practice, inexpensive.
Moreover the high-speed drilling not change the state of stresses in the material: it allows relief holes to be drilled without inducing new stresses that is very important to get a complete test.
HOW DOES IT WORK?
The hole-drilling method allows accurate experimental stress analyses at moderate costs.
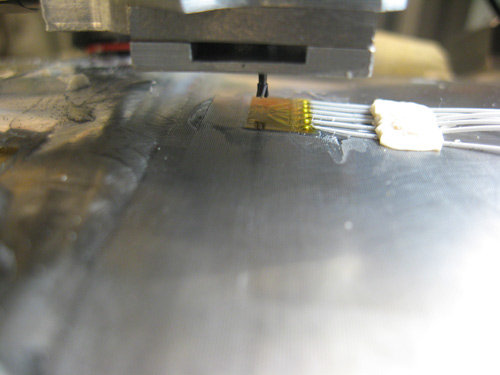
It consists in drilling a small hole (typically 1.8 – 2.0 mm) at very high speed to induce an alteration in the stress state involving a change and a redistribution of forces within the structure. This change can be measured by a strain gauge rosette with three branches, acquiring and elaborating the data to obtain the measurement of the residual stress.
The hole-drilling strain-gage method has been standardized at a world level by the ASTM E 837-13 “Standard Test Method for Determining Residual Stresses by the Hole-Drilling Strain-Gage Method”.
The ASTM E837-13 specifies the number of drilling increments required, the numerical coefficients for determining the value of residual stresses, the data processing method, the measurement-related uncertainty.
The complete hole drilling method test is made up by the following procedure:
- Installation of a three-radial grid strain gauge rosette.
- Drilling of a small hole through the center of the rosette.
- Measurement of strains produced by relaxation of the residual stresses.
- Calculation of residual stresses from the strain measurements.
In terms of cost, accuracy and versatility, this is one of the more efficient non-destructive mode of relief of residual stresses. Due to this process, it is also called the “method of the hole”.
The importance of the analysis of residual stresses
 The residual stress analysis assumes a role of fundamental importance in the phases of mechanical design.
The residual stress analysis assumes a role of fundamental importance in the phases of mechanical design.
Only through the qualitative and quantitative detection of these forces it is possible to determine which processes are most suitable for the machining of the components and the best quantity of material to use in their realization or its particular conformation, to predict and prevent malfunction or breakage.
CAUSES OF THE OCCURRENCE OF RESIDUAL STRESSES
In practice, the most common events that involve the occurrence of residual stresses are:
-
- Machining
- Forging and welding processes
- Non-uniformity of temperature in the volume of metal in the early stages of a merger or cooling
- Heating of materials during thermal treatments
- Non uniform density of the material due for example to the processes of hardening of metals
Thanks to the hole-drilling method we can determine residual stresses inside materials with a non-destructive technique.



